In the construction world, time and material flow define success. A delay in the delivery of steel, cement, or electrical supplies can halt an entire site. On the other hand, overstocking materials ties up capital and increases waste.
This is where Just-in-Time (JIT) Material Procurement steps in — a smart, lean approach to ensure materials arrive exactly when needed, not weeks before or days too late.
JIT helps builders and contractors achieve the perfect balance between availability and efficiency, reducing inventory costs and avoiding costly downtime.
What Is Just-in-Time (JIT) Material Procurement?
Just-in-Time (JIT) is a lean supply chain strategy that minimizes inventory levels by synchronizing procurement and delivery with actual project schedules.
Instead of stockpiling materials, project managers procure items in smaller quantities, scheduled to arrive “just in time” for use.
In construction, this approach demands real-time coordination among procurement teams, suppliers, transporters, and site engineers — often enabled through digital construction management systems.

Why JIT Matters for Modern Construction Projects
Construction projects today are complex, fast-paced, and multi-site. JIT material procurement provides several operational and financial advantages:
1. Reduced Inventory and Storage Costs
Traditional procurement models require bulk buying, leading to expensive warehousing, spoilage, and pilferage. With JIT, materials arrive only when required — saving up to 25-30% of storage and handling costs.
2. Improved Cash Flow
By avoiding premature bulk purchases, contractors keep working capital free for core operations. This helps maintain liquidity and financial agility throughout the project lifecycle.
3. Fewer Material Wastages
Overstocking leads to damage, obsolescence, and poor accountability. JIT reduces waste by ensuring materials match usage, improving sustainability and cost efficiency.
4. Enhanced Project Scheduling and Coordination
Because JIT aligns procurement with task schedules, it encourages teams to plan better and synchronize timelines across departments — procurement, site operations, and vendors.
5. Minimized On-Site Clutter and Safety Risks
Less material clutter means safer, cleaner, and more productive construction sites — directly improving workplace safety and site mobility.
How Digital Tools Enable JIT Procurement
Implementing JIT procurement manually can be challenging. However, digital tools make it achievable and scalable. Here’s how:
1. Real-Time Inventory and Demand Tracking
Cloud-based construction platforms provide live dashboards showing consumption rates, reorder levels, and stock positions across sites. Procurement teams can forecast needs precisely and schedule deliveries automatically.
2. Integrated Vendor Portals
Modern tools allow vendors to see upcoming requirements and update their delivery schedules proactively. This eliminates manual follow-ups and communication gaps.
3. Smart Alerts and Notifications
Automated alerts notify teams before material depletion or delay, ensuring proactive decisions rather than reactive firefighting.
4. Data-Driven Procurement Decisions
Analytics modules assess past consumption patterns, supplier reliability, and lead times — enabling smarter purchase planning and negotiation.
5. Seamless Site-to-Procurement Coordination
Field engineers can raise requisitions directly from mobile apps, while central procurement teams can approve, order, and track deliveries in real time.
Steps to Implement JIT Material Procurement in Construction
If you’re planning to move toward a JIT model, here’s a proven roadmap:
- Map Your Material Flow
Identify which materials can be sourced on a JIT basis without disrupting workflow. Bulk materials (cement, steel) may still require buffer stock.
- Collaborate with Reliable Suppliers
Choose vendors who can guarantee consistent quality and delivery timelines.
- Digitize Procurement and Inventory
Use construction management software to track demand, deliveries, and usage in real time.
- Create Predictive Schedules
Integrate project Gantt charts with procurement modules to automatically trigger purchase requests based on task progress.
- Set Performance KPIs
Monitor supplier reliability, lead times, delivery accuracy, and cost savings to evaluate the success of JIT adoption.
- Train Your Teams
Help procurement and site teams understand the lean principles behind JIT to ensure smooth adoption.
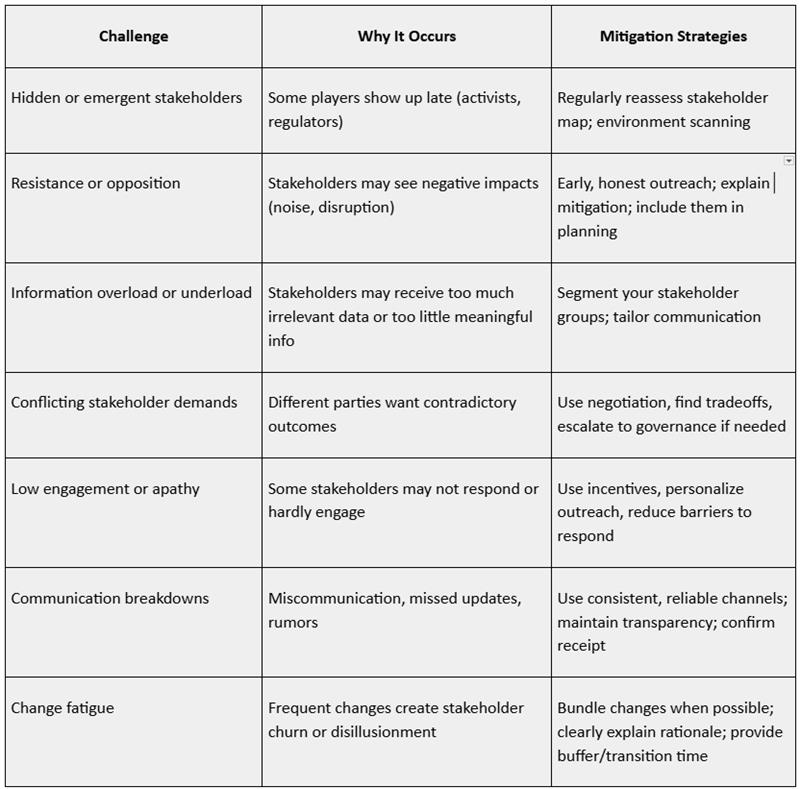
Challenges of JIT Procurement (and How to Overcome Them)
While JIT delivers high efficiency, it requires precision and digital readiness. Common challenges include:
| Challenge | Impact | Solution |
| Supplier delays | Workflow disruption | Build a network of backup vendors |
| Transportation issues | Missed deadlines | Use route tracking & logistics alerts |
| Poor forecasting | Material shortages | Leverage AI-based demand prediction |
| Lack of visibility | Communication gaps | Use centralized project dashboards |
The ROI of JIT Procurement
Companies implementing JIT procurement report:
- 20–35% reduction in inventory carrying costs
- 15–25% faster project completion through smoother coordination
- 10–20% higher cash flow efficiency
- Fewer material wastages and better sustainability metrics
Over time, these improvements translate to higher profit margins, better client satisfaction, and stronger supplier partnerships.
Conclusion: Building the Future, One On-Time Delivery at a Time
Just-in-Time Material Procurement isn’t just about reducing inventory — it’s about building a culture of precision, collaboration, and efficiency.
For construction firms adopting digital transformation, JIT is a cornerstone of lean operations. With integrated procurement dashboards, predictive analytics, and vendor collaboration, you can turn timing into your competitive advantage.
FAQs
1. What is Just-in-Time procurement in construction?
It’s a method of sourcing materials to arrive exactly when needed, reducing storage and holding costs.
2. How does JIT reduce project delays?
By synchronizing procurement with task schedules, materials are always available when required — no waiting time.
3. What type of software supports JIT procurement?
Integrated construction management platforms with modules for inventory tracking, supplier coordination, and analytics.
4. Is JIT suitable for all materials?
Not always. Critical or imported materials may need buffer stock, while consumables and short-lead materials fit JIT best.
5. What are the key benefits of JIT procurement?
Reduced costs, better cash flow, less waste, improved coordination, and safer worksites.
6. How can JIT improve sustainability?
By minimizing excess stock and wastage, it supports eco-friendly and resource-efficient construction.
7. Does JIT work for multi-site projects?
Yes, if supported by centralized procurement dashboards and strong vendor communication.
8. What KPIs track JIT success?
Inventory turnover rate, supplier lead time, delivery accuracy, and stock-out frequency.
9. Can JIT procurement work without automation?
It’s possible, but inefficient — automation ensures accuracy, transparency, and speed.
10. How does JIT impact supplier relationships?
It builds long-term, trust-based relationships through consistent collaboration and visibility.