In project-driven industries like construction, manufacturing, and engineering, the balance between procurement efficiency and inventory availability defines project success.
Delays in material delivery can halt operations, while overstocking drains cash flow and storage space.
This is where Supplier & Inventory Optimization plays a pivotal role — thereby ensuring you have the right materials, in the right quantity, at the right time, from the most reliable sources.
What Is Supplier & Inventory Optimization?
Supplier & Inventory Optimization is the strategic coordination between procurement teams, vendors, and warehouse operations to minimize delays, reduce costs, and enhance supply chain resilience.
It involves continuously analyzing supplier performance, material consumption patterns, and inventory levels to make data-driven decisions on when and how much to procure.
Simply put — it’s about striking the perfect balance between “not enough stock” and “too much stock.”

Why Balancing Procurement and Inventory Is Crucial
A well-optimized supplier and inventory ecosystem brings measurable business impact:
- Fewer Project Delays: To begin with, materials arrive exactly when needed — neither too early nor too late — thereby preventing scheduling bottlenecks and ensuring on-time progress.
- Lower Carrying Costs: Additionally, avoid locking up capital in idle inventory, which in turn helps reduce unnecessary storage expenses and optimize working capital.
- Improved Cash Flow: Moreover, real-time tracking prevents over-purchasing, leading to better liquidity and smarter financial planning across projects.
- Reduced Downtime: As a result, smart reordering mechanisms ensure zero stock-outs, allowing teams to maintain consistent productivity without interruptions.
- Reliable Supplier Network: Finally, vendors are continually evaluated based on KPIs like delivery rate, quality, and responsiveness — therefore fostering a dependable and performance-driven supplier ecosystem.
When executed properly, these improvements ripple across the project lifecycle — boosting productivity, on-time delivery, and profitability.
Key Components of Supplier & Inventory Optimization
1. Demand Forecasting
Use historical project data and consumption trends to predict upcoming material requirements. Forecasting avoids last-minute purchases and ensures procurement aligns with actual project schedules.
2. Supplier Evaluation & Rating
Evaluate vendors based on parameters such as:
- Delivery timeliness
- Material quality
- Responsiveness to change orders
- Cost competitiveness
- Compliance and certifications
Modern systems like OConstruction automate vendor scorecards and help identify high-performance suppliers.
3. Just-In-Time (JIT) Procurement
Adopt JIT principles to procure materials closer to the usage date, reducing warehouse load and carrying costs. For example, in EPC or infrastructure projects, steel or cement deliveries can be scheduled phase-wise instead of bulk orders.
4. Safety Stock & Buffer Strategy
Maintain minimal safety stock for critical materials with long lead times. This ensures work continuity in case of transportation disruptions, supplier delays, or quality rejections.
5. Integrated Procurement Scheduling
Synchronize procurement timelines with project Gantt charts and resource plans. When procurement, inventory, and project scheduling work in tandem, delays reduce drastically.
6. Inventory Visibility & Automation
Use digital inventory systems to track:
- Current stock levels
- Reserved quantities for projects
- Reorder thresholds
- Supplier lead times
Dashboards offer real-time insights, enabling proactive replenishment decisions.
How Technology Streamlines Supplier & Inventory Optimization
Modern SaaS tools like OConstruction are revolutionizing how project-based businesses manage procurement.
Key benefits include:
- Automated Reorder Triggers: To start with, get instant alerts whenever materials hit their minimum stock levels, ensuring timely replenishment and uninterrupted project progress.
- Supplier Portals: Moreover, enable vendors to upload invoices, shipment details, and certifications online — thereby improving transparency and reducing manual follow-ups.
- Material Tracking: In addition, Barcode or QR code integration ensures accurate stock movement logs, allowing teams to trace every material from procurement to usage.
- Real-Time Analytics: Furthermore, track supplier performance, lead times, and fulfillment metrics in real time, helping you identify bottlenecks and optimize sourcing strategies.
- Budget Integration: Finally, ensure every purchase order aligns with financial constraints and project budgets — therefore maintaining cost control and financial discipline throughout the project lifecycle.
These platforms bring transparency, accountability, and agility across the procurement lifecycle.
Strategies to Minimize Procurement Delays
- Multi-Vendor Sourcing: To begin with, don’t rely on a single supplier — instead, build redundancy for critical items to ensure uninterrupted material availability.
- Pre-Qualification: Next, approve vendors based on compliance, quality history, and delivery capacity before project initiation, thereby reducing risks from unreliable sources.
- Digital PO Tracking: Furthermore, implement systems to monitor every purchase order’s lifecycle — from approval to delivery — so that nothing slips through the cracks.
- Collaborative Forecasting: In addition, share project timelines and demand forecasts with suppliers to help them plan production and logistics more effectively.
- Contractual SLAs: Finally, include penalties for late delivery as well as bonuses for early or on-time supply, ensuring accountability and driving consistent supplier performance.
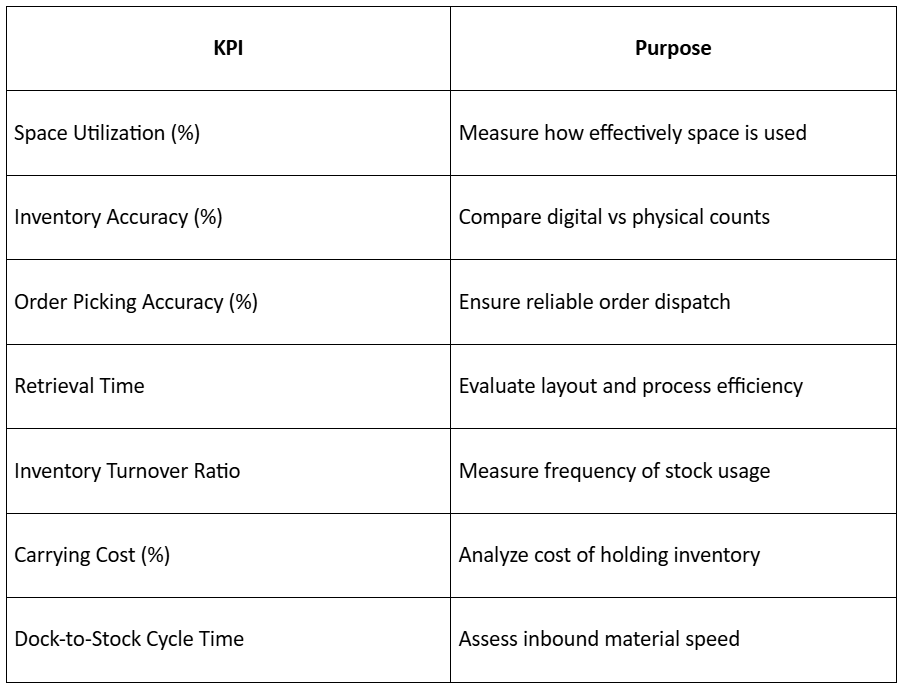
KPIs for Measuring Supplier & Inventory Optimization

Tracking these KPIs ensures continuous improvement and accountability across your procurement and warehouse ecosystem.
Use Case
Imagine a construction project with multiple subcontractors waiting for rebar and concrete. In such scenarios, even one delayed delivery can halt the entire chain — ultimately increasing idle time and cost.
However, without optimized supplier coordination, these delays become frequent and costly. That’s why using OConstruction’s Vendor & Inventory Module can make all the difference.
With this module, project managers can:
- Proactively get alerts for upcoming material requirements.
- Seamlessly issue automated POs to pre-approved vendors.
- Consistently track deliveries against work progress.
- Efficiently maintain lean yet sufficient inventory at each site.
As a result, teams achieve timely execution, reduced wastage, and enhanced supplier relationships — ensuring smoother project delivery from start to finish.
Conclusion
Supplier & Inventory Optimization isn’t just a supply-chain concern — it’s a strategic pillar of project success.
When procurement, vendors, and inventory teams collaborate through digital systems, projects stay on schedule and within budget.
The key lies in data-driven decisions, automation, and continuous performance monitoring.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is supplier and inventory optimization?
Supplier and inventory optimization is the process of aligning procurement, supplier management, and inventory control to ensure materials are available when needed — without overstocking or causing project delays. It helps balance cost, timing, and supply reliability.
2. Why is supplier optimization important in project management?
Ultimately, supplier optimization ensures you collaborate with reliable, high-performing vendors. As a result, these partners consistently deliver quality materials on time, within scope, and in full alignment with project requirements. This reduces risks like project delays, cost overruns, and rework, while improving overall operational efficiency.
3. How can inventory optimization reduce project costs?
By maintaining optimal stock levels — neither excess nor shortage — you save money on storage, avoid material wastage, and keep cash flow healthy. Smart forecasting and real-time tracking prevent costly last-minute purchases.
4. What are the key techniques used for supplier and inventory optimization?
Common techniques include:
- Demand forecasting based on project schedules
- Just-In-Time (JIT) procurement
- Supplier evaluation and rating systems
- Automated reorder points
- Safety stock planning for critical materials
5. How does technology improve supplier and inventory optimization?
Modern platforms like OConstruction integrate procurement, warehouse, and supplier data in real time. Features such as supplier portals, automated purchase orders, and stock-level dashboards enable faster, data-driven decision-making and reduce manual errors.
6. What KPIs should I track to measure supplier and inventory performance?
Key performance indicators include:
- On-time delivery rate
- Stock turnover ratio
- Procurement lead time
- Supplier quality score
- Inventory carrying cost
Tracking these metrics helps ensure continuous improvement and accountability.
7. How can Just-in-Time (JIT) procurement help minimize delays?
JIT ensures materials are delivered just before they’re needed, preventing storage bottlenecks and capital lock-up. When linked with real-time project schedules, JIT minimizes both idle time and material unavailability.
8. What are the challenges in balancing procurement and inventory?
To begin with, construction projects often face several challenges — including supplier unreliability, inaccurate demand forecasts, transportation delays, as well as poor communication between procurement and site teams. Moreover, using integrated systems helps overcome these hurdles efficiently.
9. How does OConstruction help with supplier and inventory optimization?
OConstruction Provides a unified dashboard for managing vendors, purchase orders, and inventory levels. With this integrated system, you can track supplier KPIs effortlessly, while also automating reorders to maintain optimal stock levels. Moreover, it helps align procurement activities with project timelines, ensuring that materials arrive exactly when needed. As a result, you gain real-time visibility across all sites — thereby minimizing delays and reducing wastage.
10. What’s the difference between inventory optimization and warehouse management?
Inventory optimization focuses on how much and when to stock, while warehouse management deals with how and where to store materials. Both are interconnected — optimized inventory leads to efficient warehouse operations.